A materiality assessment is a systematic process that identifies, evaluates, and prioritizes the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues that are significant to a company and its stakeholders. The goal of this assessment is to determine which factors have the potential to impact the organization’s financial performance and reputation, as well as which aspects are of utmost importance to stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and the community at large.
Why Should Businesses in Malaysia Focus on Materiality Assessments?
In Malaysia’s evolving business landscape, enhancing ESG performance is more important than ever. A robust materiality assessment serves as the cornerstone of effective ESG strategy. By identifying and prioritizing sustainability issues that matter most to your stakeholders and business success, it allows companies to align their ESG initiatives with real-world risks and opportunities.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the strategic approach to materiality assessment, specifically tailored for the Malaysian context.
Whether you’re just starting your ESG journey or looking to refine your existing approach, this guide will help you:
- Understand the materiality concept and its application
- Master proven assessment methodologies
- Navigate stakeholder engagement effectively
- Implement best practices for sustainable business growth
Let’s dive in and transform your ESG strategy through well-executed materiality assessment.
Looking to prioritize the right ESG factors for your business success?
A comprehensive materiality assessment ensures you’re focused on what truly matters to your stakeholders and operations.
- What Is a Materiality Assessment and Why Is It Important for Businesses?
- How Can Companies Conduct a Comprehensive ESG Materiality Assessment?
- How Does a Materiality Assessment Help Organizations Prioritize ESG Issues?
- What Is Double Materiality in ESG Reporting, and Why Is It Becoming More Important for Companies?
- How Do Regulatory Compliance and Global Standards Shape ESG Practices and Corporate Governance?
- What Challenges Do Companies Face When Conducting a Materiality Assessment, and How Can They Overcome Them?
- What Are the Best Practices for Implementing ESG Principles in Organizations?
- How Wellkinetics Can Help
What Is a Materiality Assessment and Why Is It Important for Businesses?
Materiality assessment serves as a cornerstone for organizations aiming to identify and prioritize environmental, social, and governance factors that significantly impact their business operations and stakeholders. This strategic process helps companies focus their sustainability efforts on areas that matter most to their success and stakeholder interests.
How Can Companies Conduct a Comprehensive ESG Materiality Assessment?
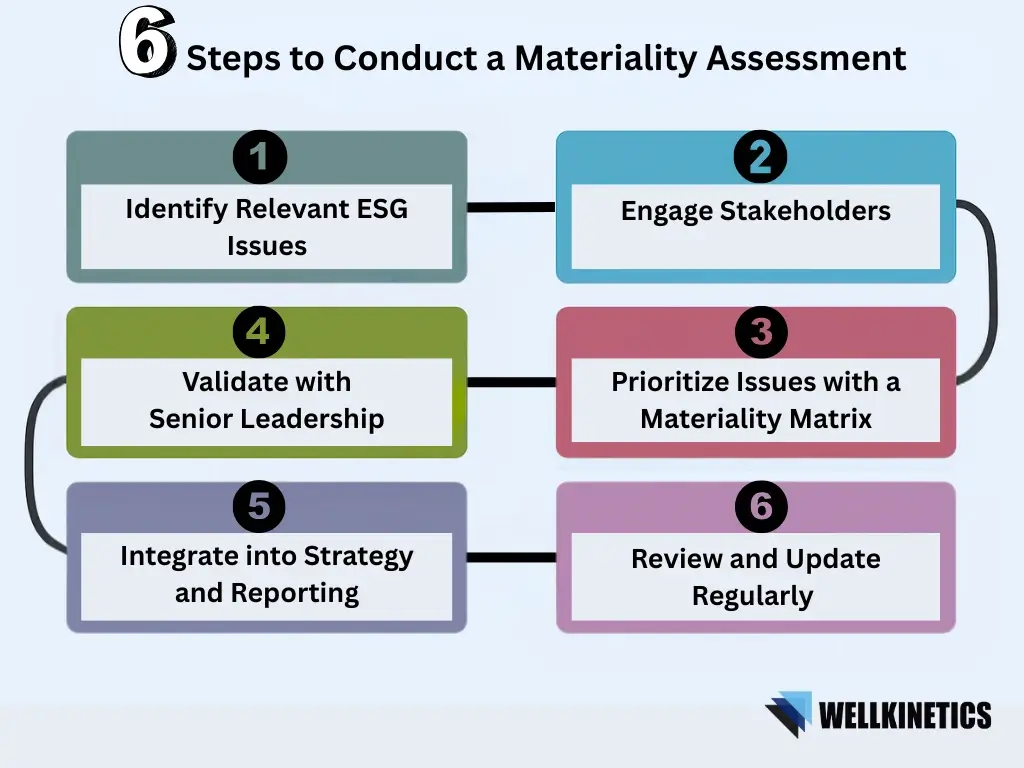
To conduct a comprehensive ESG materiality assessment, companies must first define what ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) materiality means for their specific context. It involves identifying and prioritizing the environmental and social issues that are most relevant to the organization’s operations, stakeholders, and long-term value creation. The process typically includes steps such as:
1. Identify Relevant ESG Issues
The process begins with identifying a broad list of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) topics that could be relevant to the organization. This involves reviewing global reporting frameworks such as GRI, SASB, ISSB, or CSRD, as well as considering peer practices, stakeholder expectations, internal policies, and emerging risks. The goal is to ensure a comprehensive understanding of ESG issues that may have a direct or indirect impact on the business or society.
2. Engage Stakeholders
Once the list of ESG issues is developed, the organization engages with key stakeholders to gather their views on which issues are most important. Stakeholders may include employees, management, board members, investors, customers, suppliers, regulators, and communities. Engagement methods can range from surveys and interviews to workshops or focus groups. This step ensures that the materiality assessment reflects a broad range of perspectives and expectations.
3. Prioritize Issues (Materiality Matrix)
With stakeholder input gathered, the next step is to prioritize the ESG issues based on two key criteria: the level of concern to stakeholders and the potential impact on the organization. These issues are then plotted on a materiality matrix, a visual representation that highlights which topics are most critical. Some organizations may also apply a “double materiality” lens, considering both how ESG issues affect the business and how the business impacts the environment and society.
4. Validate with Leadership
After prioritizing the ESG issues, the findings should be reviewed and validated with senior management. This step ensures that the prioritization aligns with the organization’s overall strategy and long-term goals. Senior leadership plays a key role in confirming that the most material topics have been correctly identified and that the assessment reflects the business’s true priorities. Any necessary adjustments can be made at this stage to ensure that the materiality matrix is fully aligned with the company’s vision.
5. Integrate into Strategy & Reporting
Once validated, the prioritized material topics are integrated into the organization’s ESG or sustainability strategy. This includes setting relevant goals and performance indicators, developing action plans, and shaping the structure of ESG or sustainability reports. The material topics also help guide stakeholder communication, resource allocation, and long-term risk management.
6. Review and Update Regularly
Materiality is not a one-off exercise. Organizations should revisit and update the materiality assessment periodically, typically every 1 to 2 years or when there are major changes in the business environment, regulatory landscape, or stakeholder expectations. Regular reviews help ensure that the ESG strategy remains relevant, forward-looking, and responsive to change.
How Does a Materiality Assessment Help Organizations Prioritize ESG Issues?
A materiality assessment serves as a strategic tool for organizations to identify and prioritize ESG issues that matter most to their stakeholders and business success. This systematic approach helps companies focus their sustainability efforts where they can create the most impact, ensuring efficient resource allocation and meaningful progress.
What Are the Key Benefits of Conducting a Materiality Assessment?
Understanding the key drivers of ESG performance through materiality assessments enables organizations to make informed decisions about their sustainability initiatives. Companies that conduct thorough materiality assessments often experience:
- Enhanced stakeholder trust and engagement
- Improved risk management capabilities
- Better alignment of sustainability initiatives with business objectives
- More focused and effective ESG reporting
- Increased competitive advantage in the market
By establishing clear ESG priority areas, organizations can develop targeted strategies that deliver measurable results.
The assessment process also helps identify potential risks and opportunities early, allowing companies to proactively address challenges before they impact business operations.
Moreover, materiality assessments enable better resource allocation by helping organizations focus their efforts on initiatives that create the most value.
What Is Double Materiality in ESG Reporting, and Why Is It Becoming More Important for Companies?
As ESG reporting standards continue to evolve, the concept of double materiality is becoming increasingly significant, offering a comprehensive framework that considers both financial and impact perspectives.
Unlike traditional financial reporting, which focuses solely on investor-related risks, double materiality considers:
- Financial materiality: How sustainability issues affect the company’s financial performance.
- Impact materiality: How the company’s activities affect society and the environment.
Double materiality has become especially important with the introduction of frameworks like the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which mandates this approach for qualifying companies. It reflects the growing expectations of stakeholders (investors, regulators, customers, and communities) who want transparent reporting on both financial risks and broader societal impacts.
How Does Financial Materiality Influence a Company’s Performance and ESG Strategy?
Financial materiality focuses on how environmental and social factors affect a company’s financial performance and value creation. This perspective examines financial risk and opportunities that could impact business operations, revenue, and long-term sustainability. Through ESG materiality analysis, organizations can identify and assess factors that may influence investor decisions, market position, and overall financial health.
Companies implementing financial materiality assessments gain deeper insights into potential risks and opportunities that could affect their bottom line. This approach helps businesses make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic planning while meeting stakeholder expectations for transparent financial reporting.
Financial materiality represents one half of the double materiality approach emphasizing the inward impact of sustainability factors on the business itself.
What Is Impact Materiality and How Does It Shape a Company’s Sustainability Strategy?
Impact materiality examines how an organization’s activities affect the environment, society, and economy. This perspective goes beyond financial considerations to evaluate the broader implications of business operations.
This assessment considers factors such as carbon emissions, biodiversity impact, labor practices, and community relations. By understanding these impacts, companies can develop more effective sustainability strategies and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
Together with financial materiality, this outward-looking perspective ensures companies evaluate ESG issues from both sides of the equation (financial risks and real-world impacts) making double materiality a powerful tool for sustainable strategy and reporting.
Ready to gain a complete understanding of your ESG impact?
The double materiality approach provides a thorough analysis of both financial and social/environmental factors, guiding your strategic sustainability decisions.
How Do Regulatory Compliance and Global Standards Shape ESG Practices and Corporate Governance?
The need for ESG materiality assessments is not just a best practice; it’s quickly becoming a regulatory expectation. Around the world, governments, stock exchanges, and international bodies are setting clearer rules and frameworks for how companies report on sustainability.
In Malaysia, the evolving ESG reporting landscape signals a significant shift in corporate governance practices, especially with the introduction of the National Sustainability Reporting Framework (NSRF). This new framework, that is set to aligned closely with IFRS S1 and S2 established by International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), is not just a regulatory update; it represents a significant transformation in how companies approach sustainability within their business operations.
As Malaysia joins other leading economies in adopting international frameworks, the focus on materiality, regulatory compliance, and the use of global standards is reshaping the corporate landscape.
How Does the National Sustainability Reporting Framework (NSRF) Affect Non-Listed Companies in Malaysia?
Previously, sustainability reporting was primarily a requirement for public-listed companies (PLCs) on Bursa Malaysia. However, under the NSRF, the obligation to submit sustainability reports has been extended to large non-listed companies (NLCos) with annual revenues surpassing RM2 billion. This shift brings Malaysia in line with international counterparts like the UK, Singapore, and the EU, recognizing that sustainability risks affect the broader economy, not just publicly traded entities.
The expansion of reporting requirements means that many NLCos will now be required to disclose their sustainability efforts, ensuring a more comprehensive approach to ESG reporting across Malaysia’s economy. This move emphasizes a “whole-of-society” approach, ensuring that transparency is not limited to PLCs but extends throughout the value chain, including large private companies.
What Are IFRS S1 and S2, and How Do They Influence Sustainability Reporting in Malaysia Under the NSRF?
At the heart of the NSRF is the requirement for companies to adhere to the ISSB’s standards, specifically IFRS S1 and IFRS S2.
- IFRS S1: General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-related Financial Information
Requires companies to disclose material sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could affect their prospects. - IFRS S2: Climate-related Disclosures
Specifically addresses climate-related risks and opportunities, following the TCFD structure: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics/targets.
These standards are designed to provide a global framework for sustainability reporting, ensuring that companies disclose how sustainability risks and opportunities can impact their financial performance and operations in the short, medium, and long term.
Why Is Materiality Important in IFRS S1 and S2 Reporting, and How Does It Influence Business Decision-Making?
Materiality is a key concept within both IFRS S1 and S2, ensuring that the reported information is relevant and impactful for investors. Both standards emphasize financial materiality meaning companies must assess and disclose what’s material to enterprise value. This means that companies must conduct a materiality assessment to determine which sustainability topics to report on and what risks and opportunities influence financial performance and strategy.
For businesses, determining what constitutes material information requires careful consideration of the sustainability risks and opportunities that could influence their financial performance, access to capital, and operational resilience.
Materiality assessments ensure that companies focus on the most relevant ESG factors to their industry, value chain, and stakeholder interests. This focus helps organizations prioritize the reporting of the most impactful data, avoiding information overload and providing investors with clear insights into the company’s sustainability performance.
ALSO READ: Sustainability Frameworks: A Guide to Global Standards and Their Application in Malaysia
What Challenges Do Companies Face When Conducting a Materiality Assessment, and How Can They Overcome Them?
As sustainability reporting moves from voluntary to mandatory, materiality assessments are no longer just “nice to have”; they’re the backbone of credible disclosures. Standards like IFRS S1 and S2 and Malaysia’s upcoming National Sustainability Reporting Framework (NSRF) place materiality at the center of sustainability strategy.
Conducting a successful materiality assessment often faces several hurdles that organizations must navigate carefully.
1. Translating Global ESG Themes into Business-Relevant Topics
Challenge: Companies often start with broad topics (e.g., climate change, human rights) but struggle to identify which ones genuinely affect their operations or strategic goals.
Solution: Use peer benchmarking, industry-specific standards, and investor feedback to ground materiality in business relevance.
2. Balancing Financial and Impact Materiality
Challenge: With different frameworks emphasizing different lenses, companies can be unsure how to structure their materiality process.
Solution: Clearly define the intended audience and purpose of the report. IFRS-aligned disclosures should prioritize enterprise value, while broader sustainability or integrated reports can incorporate double materiality.
3. Engaging Stakeholders Effectively
Challenge: Stakeholder fatigue is real. Generic surveys or one-off interviews often fail to capture meaningful input.
Solution: Focus on quality over quantity. Use targeted engagement tools (e.g., issue-specific workshops, materiality scoring) and close the loop by reporting back how stakeholder input shaped decisions.
4. Limited Internal Capacity
Challenge: Many organizations lack the in-house expertise, systems, or time to conduct a robust assessment.
Solution: Invest in ESG training, build cross-functional teams, and where needed, engage external consultants to guide the process.
How Can Materiality Assessment Findings Be Effectively Integrated into Business Operations?
Effective integration of materiality assessment findings into business operations is crucial for long-term success. Start by aligning assessment outcomes with your organization’s strategic objectives and key performance indicators.
- Create clear communication channels between departments to ensure materiality insights inform decision-making at all levels. This approach helps embed ESG considerations into daily operations rather than treating them as standalone initiatives.
- Develop a robust monitoring system to track progress on material issues. Regular reviews and updates ensure your sustainability effort remains aligned with evolving stakeholder expectations and market dynamics.
- Establish accountability measures by assigning specific responsibilities to senior management for implementing assessment recommendations. This top-down approach demonstrates your organization’s ESG commitment and drives meaningful change.
- Consider creating cross-functional teams responsible for implementing materiality-driven initiatives. These teams can help break down silos and ensure coordinated action across the organization, leading to more effective outcomes in your sustainability journey.
Ready to ensure your business complies with Malaysia’s ESG regulations?
Regulatory compliance is key to sustainable practices and maintaining stakeholder trust. Let us help you align your ESG strategies with local and international standards.
What Are the Best Practices for Implementing ESG Principles in Organizations?
Implementation best practices refer to established methods and strategies that organizations can follow to effectively incorporate ESG principles into their operations and reporting processes. These practices offer a structured approach to integrating sustainability considerations into decision-making frameworks, ensuring that companies not only comply with regulatory requirements but also enhance their overall performance.
To effectively integrate ESG principles into business operations, companies should follow these best practices:
- Align materiality findings with business strategy and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Foster cross-departmental collaboration to ensure that ESG goals are consistently applied
- Develop a monitoring system to track progress on ESG initiatives
- Assign accountability to senior management to drive ESG initiatives forward
By adopting these best practices, companies can move beyond compliance and create long-term value for both their business and society. A structured and transparent ESG implementation process not only enhances corporate reputation but also strengthens investor confidence and operational resilience.
How Wellkinetics Can Help
At Wellkinetics, we understand that navigating the complexities of materiality assessments can be a daunting journey for many organizations. Our expertise lies in guiding businesses through this process, ensuring that your sustainability initiatives not only meet regulatory standards but also align with global best practices. Here’s how we can assist you:
1. Tailored Consultation Services: We provide personalized consultations to help you conduct effective materiality assessments that are specific to your industry and stakeholder landscape. Our team of experts will work closely with you to ensure that you engage diverse stakeholder groups and capture their insights effectively.
2. Training and Capacity Building: Recognizing that internal expertise is essential, we offer specialized training programs for your teams. Our workshops are designed to equip your staff with the necessary skills to gather accurate data, analyze results, and implement materiality assessments seamlessly.
3. Data Collection Support: With structured methodologies in place, we help ensure that your data is of the highest quality and aligned with recognized reporting frameworks.
4. Integration Strategy Development: We assist in embedding ESG considerations into your corporate strategy. Our experienced consultants will work with you to ensure that materiality findings align with your organizational goals, thus fostering a culture of sustainability across all levels of your business.
5. Ongoing Monitoring and Review: We believe that a successful ESG strategy requires continual assessment and adjustment. We offer ongoing support to help you monitor your ESG initiatives, ensuring they remain effective and relevant in response to shifting stakeholder expectations and market trends. Our team will work with you to establish key performance indicators, review outcomes, and adjust strategies as necessary, so your organization can adapt effectively to an evolving business landscape.
6. Comprehensive Reporting Solutions: Transparency is vital for building trust with stakeholders. We assist you in creating comprehensive reports that effectively communicate your ESG efforts and materiality assessment results. Our tailored reporting solutions ensure compliance with leading international standards while effectively showcasing your commitment to sustainability.
7. Stakeholder Engagement Strategies: Engaging your stakeholders is critical to the success of your materiality assessment. We provide guidance on best practices for engaging various groups, ensuring their voices are heard and their concerns are addressed in your ESG strategy. This not only strengthens stakeholder trust but also enhances the legitimacy and effectiveness of your initiatives.
8. Benchmarking and Best Practices: Utilizing our extensive knowledge of industry standards, we offer benchmarking services that compare your organization against peers and industry leaders. By learning from best practices, you can enhance your ESG performance and stay ahead of emerging trends.
Learn more about our corporate governance solutions.




